Iterate function
Folds values from an event stream into a signal.
Syntax
// (1)
template
<
typename D,
typename E,
typename V,
typename F,
typename S = decay<V>::type
>
Signal<D,S> Iterate(const Events<D,E>& events, V&& init, F&& func);
// (2)
template
<
typename D,
typename E,
typename V,
typename F,
typename ... TDepValues,
typename S = decay<V>::type
>
Signal<D,S> Iterate(const Events<D,E>& events, V&& init,
const SignalPack<D,TDepValues...>& depPack, F&& func);
Semantics
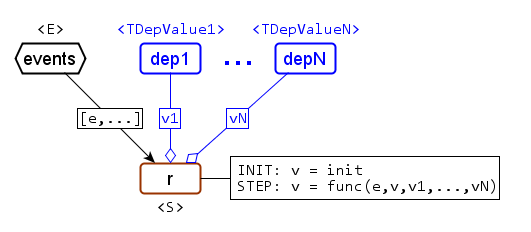
(1) Creates a signal with an initial value v = init.
-
If the return type of func is S: For every received event e in events, v is updated to v = func(e,v).
-
If the return type of func is void: For every received event e in events, v is passed by non-cost reference to func(e,v), making it mutable.
This variant can be used if copying and comparing S is prohibitively expensive.
Because the old and new values cannot be compared, updates will always trigger a change.
(2) Similar to (1), but the synchronized values of signals in depPack are passed to func as additional arguments. Changes of signals in depPack do not trigger an update - only received events do.
The signature of func should be equivalent to:
- (1a)
S func(const E&, const S&)
- (1b)
void func(const E&, S&)
- (2a)
S func(const E&, const S&, const TDepValues& ...)
- (2b)
void func(const E&, S&, const TDepValues& ...)
The event parameter const E& can also be replaced by an event range, i.e. S func(EventRange<E> range, const S&) for case (1a).
This allows for explicit batch processing of events of a single turn.
Graph
(1a)

(2a)
 Hold
Hold Monitor
Monitor Iterate
Iterate Snapshot
Snapshot Pulse
Pulse Changed
Changed ChangedTo
ChangedTo WeightHint
WeightHint Continuation
Continuation TransactionStatus
TransactionStatus DoTransaction
DoTransaction AsyncTransaction
AsyncTransaction MakeContinuation
MakeContinuation REACTIVE_DOMAIN
REACTIVE_DOMAIN USING_REACTIVE_DOMAIN
USING_REACTIVE_DOMAIN Token
Token Events
Events EventSource
EventSource TempEvents
TempEvents EventRange
EventRange MakeEventSource
MakeEventSource Merge
Merge Filter
Filter Transform
Transform Process
Process Join
Join Flatten
Flatten Tokenize
Tokenize ObserverAction
ObserverAction Observer
Observer ScopedObserver
ScopedObserver Observe
Observe Reactor
Reactor MakeReactor
MakeReactor Signal
Signal VarSignal
VarSignal TempSignal
TempSignal SignalPack
SignalPack MakeVar
MakeVar MakeSignal
MakeSignal Flatten
Flatten With
With REACTIVE_PTR
REACTIVE_PTR REACTIVE_REF
REACTIVE_REF
